Introduction
Commodities are those natural resources, good or raw materials, which are uniform in nature (there maybe differences in quality). Basically, these are used to create finished goods and services such as wheat, corn, petrol, diesel, natural, precious metals (Platinum, Palladium, Silver and Gold) and basic metals. Commodities are traded on market irrespective of their origin, for example: if a person is living in India, who is consuming petrol or natural gases for his vehicles. He does not know about the origin of these commodities; he just wants to fulfil his needs.
“From the taste of wheat, it is not possible to tell who produced it, a Russian Surf, a French peasant or an English Capitalist ".
- Karl Marx
There are four types of key costs to own a physical commodity, and that are financing, transportation, storage and insurance. Brent crude oil, Steel, WTI crude oil, Soybeans, Iron, Corn, Gold, Aluminum, Copper and Silver are the top ten traded commodities.
Market Structure
There are two types of market on the basis of transaction mechanisms

- OTC (Over the Counter): The market where transactions take place between two parties directly or without any broker or any other third party, known as Over the Counter or OTC market. It is also known as decentralized market.
- Exchange Market: The market where transactions take place between two or more parties indirectly or broker or any third party, known as exchange market. It is also known as centralized market.
In case of commodity market, the transactions take place in both of the markets, Exchange and OTC (Over the Counter) markets.
Types of Commodities
There are two types of commodities:
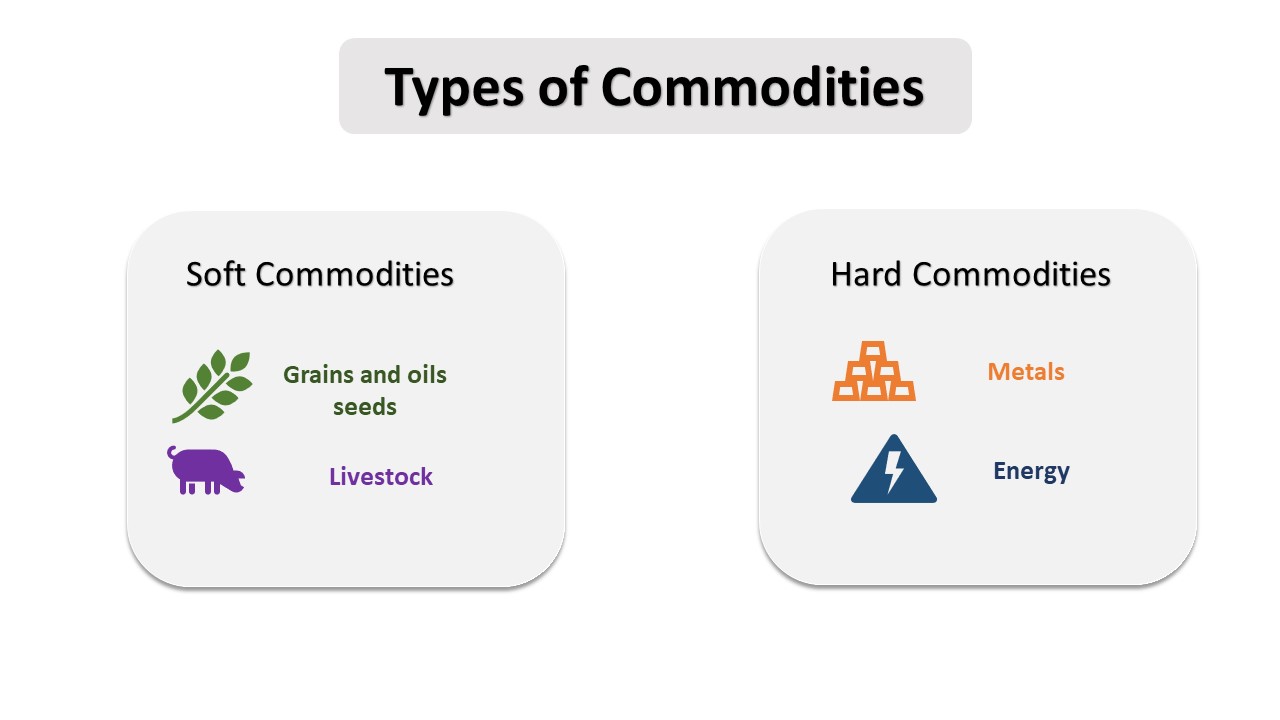
- Soft Commodities
- Hard Commodities
Soft commodities include grown commodities such as grains and oil seeds (Lumber, Cotton, Sugar, Coffee and cocoa), and it also include livestock such as Beef and Pork (Lean Hogs). It is also known as Softs, both of the live stocks and most of the agricultural commodities in Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME). In India, commodities trade on Multi Commodity Exchange of India (MCX).
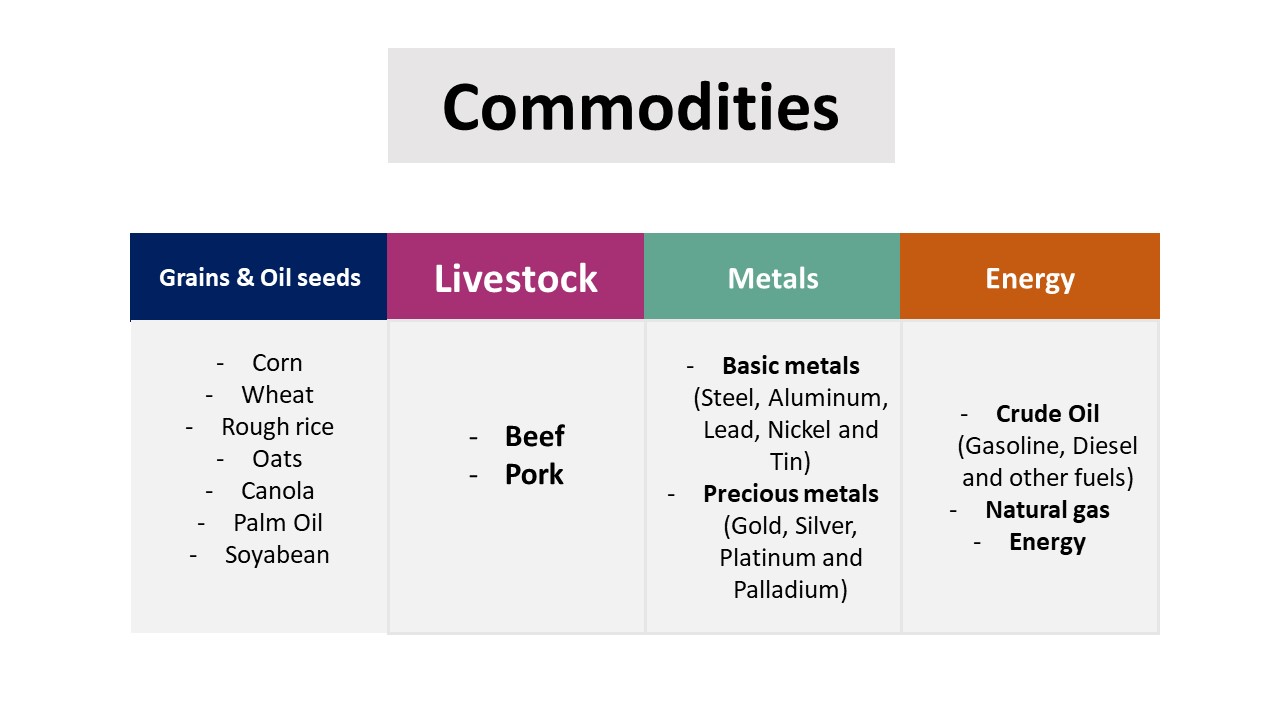
Hard Commodities include basic metals (Steel, Copper, Aluminum, Lead, Nickel, and Tin), Precious metals (Gold, Silver, Platinum and Palladium) and energy related commodities such as crude oil (Gasoline, Diesel and other fuels), natural gases and electricity. These commodities are mostly traded on CME, New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX), Intercontinental Exchange (ICE), London Metal Exchange (LME) and European Energy Exchange (EEX).
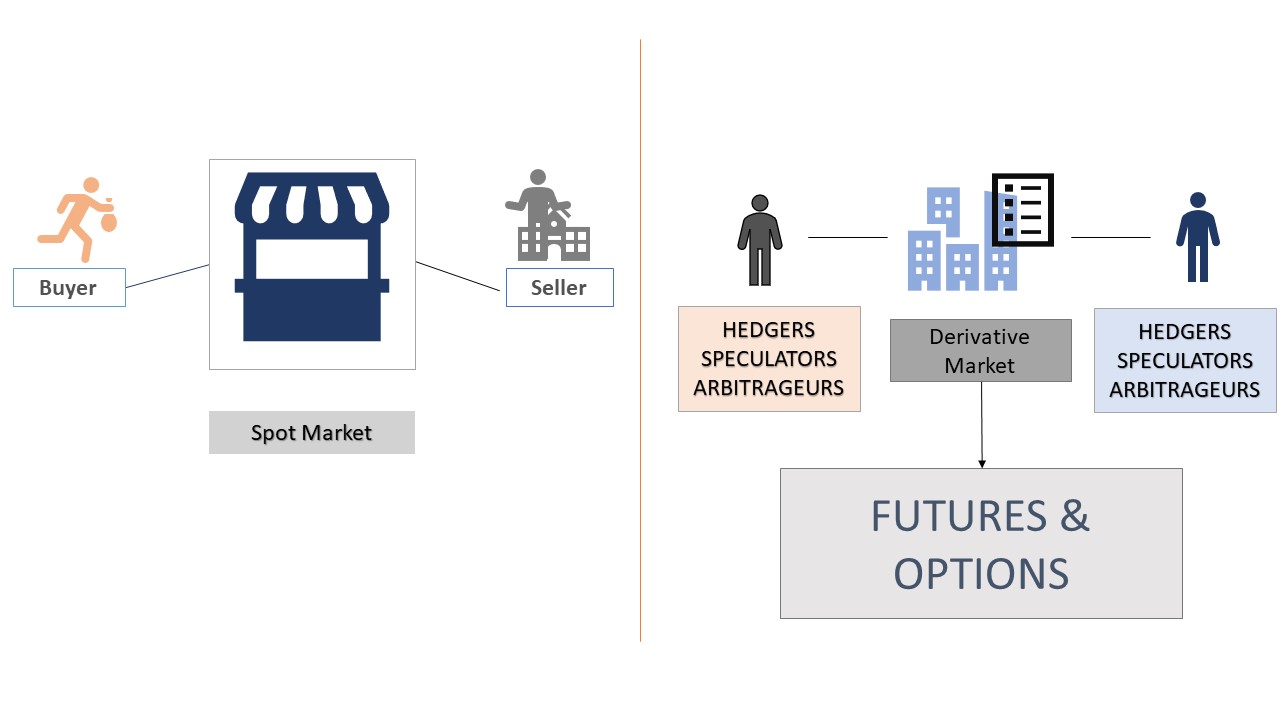
Spot and Derivative Market
People trade commodities in both of the markets, Spot and Derivative Market. In Spot Market, trades are done at the same moment. While in derivative markets, traders (Hedgers, Arbitrageurs and speculators) trade the commodities to earn profit through commitment letters or contract like futures and option. Commodities future prices can be calculated from the spot market.
Carry returns
- Convenience
- Coupons
- Dividends
Carry costs
- Financing
- Transportation
- Storage
- Insurance
Powered by Froala Editor



